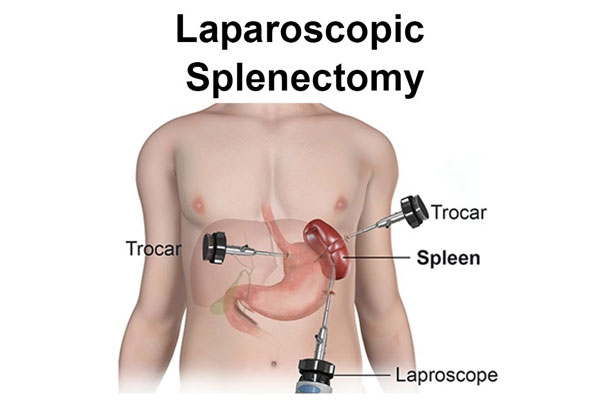
A splenectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the spleen, a small organ located on the left side of the abdomen, under the ribcage. The spleen plays a role in filtering the blood, storing platelets, and helping the body fight infections. There are various reasons why a splenectomy might be performed, including:
Trauma: In cases of severe injury to the spleen due to accidents or trauma, a splenectomy may be necessary to control bleeding or prevent further damage.
Splenomegaly: Enlargement of the spleen, often due to various medical conditions, can lead to discomfort and a reduction in blood cell counts. A splenectomy may be performed to alleviate these symptoms.
Blood Disorders: Some blood disorders, such as hereditary spherocytosis, thalassemia, and immune thrombocytopenia (formerly known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura or ITP), can be treated by removing the spleen, which is involved in breaking down blood cells.
Certain Cancers: In cases of splenic tumors or cancers, a splenectomy might be recommended as part of the treatment plan.
Infections: Rarely, in cases of severe or life-threatening infections, especially in individuals with compromised immune systems, a splenectomy may be performed to prevent the spread of the infection.
There are different surgical techniques for splenectomy, including open surgery, laparoscopic (minimally invasive) surgery, and robotic-assisted surgery. The choice of technique depends on various factors, including the patient's overall health, the reason for the procedure, and the surgeon's expertise.
After a splenectomy, individuals are at an increased risk of certain infections, particularly from encapsulated bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae. As a result, patients may receive vaccinations and antibiotics to help prevent these infections. They are also advised to take certain precautions, such as avoiding activities that may increase the risk of injury, given the spleen's role in the immune system.
It's important to discuss the specifics of a splenectomy, including the risks and benefits, with a healthcare provider if this procedure is recommended. The necessity for a splenectomy and the post-operative care will depend on the individual patient's condition and medical history.
